A GLOSSARY
Executive Field Guide to the
Sometimes-Confusing Terms found in
Industrial System Integrator Quotes
153 Acronyms + 458 Terms + 23 Illustrations
168 definitions still pending
Use our glossary in multiple ways
Relationship Tree View of Terms
Alphabetical List of Terms
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
Physical Layer>
A legacy, but very successful, Ethernet over twisted pair cables at 10 megabits per second.
It is defined in the 1990 IEEE 802.3i standard.
In the OSI reference model it is a physical layer standard.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
Physical Layer>
Ethernet over twisted pair cables at 100 megabits per second.
Also called Fast Ethernet.
It is defined in the IEEE 802.3 family of standards.
In the OSI reference model it is a physical layer standard.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
Physical Layer>
Ethernet over twisted pair cables at 1 gigabits per second.
Also called Gigabit Ethernet.
It is defined in the IEEE 802.3 family of standards.
In the OSI reference model it is a physical layer standard.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
Physical Layer>
Ethernet over twisted pair cables at 10 gigabits per second.
Also called 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
It is defined in the IEEE 802.3 family of standards.
In the OSI reference model it is a physical layer standard.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
The SLC generation of Rockwell Automation IO products.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
The Logix generation of Rockwell Automation IO products.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
The PLC5 generation of Rockwell Automation IO products.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
The Flex generation of Rockwell Automation IO products.
See One Pole Dual Toggle.
Standards organization>
A technical society that creates voluntary consensus standards for hygienic design.
The name originates from the three professional groups International Dairy Foods Association (processors),
Food Processing Suppliers Association (equipment fabricators),
and the International Association for Food Protection (regulatory sanitarians)
that came together to create better equipment design.
It does not do any product testing.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
A Schneider Electric legacy generation of field I/O products.
Hardware>
Connector>
Technically correct name for the modular 8-pin jack used for Ethernet cables in networks.
Its name derives from eight positions eight contacts.
One of the modular connector styles originating from the Bell System.
Originally and commonly called an RJ-45 connector.
Typically used with Catagory cable.
See Allen-Bradley.
See ASEA Brown Boveri.
Software>
Human Machine Interface>
A set of guidelines for HMI screen & alarm design to improve effectivity and avoid information overload.
The ASM consortium is a group of end users, consultants and universities led by Honeywell.
Any plant concerned with reducing down time and preventing product loss should explore using ASM technology in their HMI design.
Good looking HMI screens are not a guarantee of good human factors in the display design.
Hardware>
A physical device that can be commanded to move using electric, pneumatic or hydraulic power.
Networking>
Network>
A type of simplified, slower and lower-cost fieldbus used for digital inputs and outputs (OFF-ON) only.
It is not uncommon to see an ASI network being used to handle some IO for an Ethernet network.
Hardware>
Automation control>
Used as either an API (Application Program Interface) that allows interfacing the PLC to a specific piece of custom hardware,
or to simplify the coding of common rungs of code in ladder logic that are used repeatedly.
See:
1. Analog Input. (for hardware usage)
2. Artificial Intelligence. (for software usage)
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Clean In Place>
A method of clearing and drying a pipeline by using a medium-pressure high-volume air source. The fast moving air pushes out all the pipe contents and
as the pressure drops down to atmosphere the remaining liquid films evaporate. A newly welded pipe may take a number of air blow cycles to clean out all the
welding dreck. After a CIP cycle the air blow system is designed to clear the pipes in one or two air blow cycles at most.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A combination of filter, regulator, pipe fittings and mounting bracket that clean up the air from a compressor and deliver it at a constant pressure.
Often a dryer is added after the air set immediately downstream from the compressor to remove the water that condenses out as the warm air from the compressor cools down.
It is recommended practice to put an addition air set just before the devices consuming the air as addition dreck and water can be picked up
in the long pipes between the air supply and the air usage. A well designed system of air sets will increase plant reliability and OEE.
Electronics>
In hardware - a signal that indicates that a sensor has detected a parameter to be beyond its acceptable range.
In software - A notification from the control system that an operator needs to do something.
Information that does not require operator intervention should be sent to a log file instead of being displayed on any operator screen.
Hardware>
Automation control>
One or more sensor values or machine states that will trigger an alarm.
Sensor values that are out of bounds do not necessarily need to trigger an alarm but should be recorded in a log file.
Software>
Human Machine Interface>
The coordination of all alarms produced by the control system so that no more are triggered in a set amount of time than an operator can reasonably process.
Preferably no more than 2 alarms in ten minutes.

 Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
Former name (from 1910-1985) of the company that turned into Rockwell Automation. Now their best known brand.
The logo represents the outline of their nearly indestructible octagonal pilot device they are well known for.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
A Schneider Electric current generation of (Variable Frequency Drive) products.
Standards organization>
A technical society that accredits American organizations creating voluntary consensus standards to make sure they follow consistent, fair and usable standards.
It represents all American standards creating bodies at ISO.
It does not create standards itself nor does it do any product testing.
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of electrical current. Often shortened to Amp.
It is one of the seven base units of the International System of Units.
The ISO/IEC 80000 standard defines an Ampere as 6.24×1018 electrons per second.
For some perspective the number of free electrons in a cubic millimeter of copper is 84×1018 and
an individual electron in a copper wire travels at about 1 centimeter per second.
The power lost (as heat) through a conductor of a finite resistance is equal to the the square (power of two) of the current.
To minimize losses in power transmission systems the current is kept as low as possible by making the voltage as high as possible.
In a loop circuit, while voltage can change along the path due to the resistance in encounters,
the current entering a loop is the same as what exits the loop as charge cannot be created or destroyed.
As such, an analog signal sent down a long wire loop where the intended value being sent is proportional to the
current transmitted remains constant regardless of the resistance (wire length).
This is the basis and key advantage for current based instrumentation communications loops such as the common 4-20mA system.
Where mA means milliAmpere or one thousands of an Ampere.
Hardware>
Sensor>
A circuit that accepts an analog signal and turns it into a digital signal for use by the control system.
Designed to accommodate a specific range of voltages and currents.
The circuit typically includes an amplifier to scale the input voltage to the right level,
a filter to remove electrical noise, and and analog to digital converter (ADC).
Similar to:
Analog Output
Digital Input
Digital Output
Hardware>
Sensor>
A circuit that creates an analog signal from a digital signal from the control system.
Designed to output a specific range of voltages and currents.
Circuit is specifically called and digital to analog converter (DAC).
Similar to:
Analog Input
Digital Input
Digital Output
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of length that is 10-10 meters.
Its abbreviation is Å.
It is used for sizes of atoms and wavelengths of light.
See Analog Output.
See Add On Instructions.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
The seventh and highest layer of the OSI Model of networking.
It deals with the overall user-to-user, user-to-host or host-to-host communications.
Typical functions are electronic mail, file transfer, or web browser.
Hardware>
Equipment used to perform machine control or process control.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
OEM of PLCs, VFDs, motors, instrumentation, robots & automation solutions.
Incorporates the assets of some well known brands: Baldor, General Electric Industrial Solutions,
Thomas & Betts, K-Tek, B&R, Elsag-Bailey, Westinghouse Electric Transmission & Distribution, Cincinnati Milacron Robots, & Power-One.
Their documentation is well known for clarity and exceptional graphics quality.
 Engineering standard>
Engineering standard>
Appareils destinés à être utilisés en ATmosphères EXplosives (French for Equipment intended for use in ATmospheres EXplosive).
Two EU directives (laws) describing the minimum safety requirements of the workplace and equipment used in explosive atmosphere.
One directive 2014/34/EU is for the manufacturer and the other one 1999/92/EC is for the user of the equipment.
There is a similar set of requirements in the US through the National Electric Code (NEC)
Software>
One of the specific people allowed to access a particular process control function in the control system.
Current computer technology allows access control down to the specific function level for each operator.
Security is best assured when only specific operators are allowed to access each control function.
Emergency stop and other safety functions should never have access controls apart from physical guards that prevent accidental triggering.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
Industrial software manufacturer headquartered in Cambridge, England.
60% owned by Schneider Electric.
New owners of the Wonderware line of products.
Hardware>
Connector>
A series of connectors wired in parallel, usually as part of a printed circuit board,
that allow communication between the devices plugged into those connectors via some form of parallel bus or network.
In PLC usage the backplane is the enclosed printed circuit board at the back of a PLC that allows various modules to be
plugged in and thus communicate with each other and the master controller as well as get power from the backplane.
Typical design uses a set of parallel electrical conductors called a bus.
Each individual connector location is called a rack slot.
Its origin is the plane of wiring on the back wall of an enclosure that all the electronic modules plug into.
Its usage predates printed circuit boards and parallel buses.
System Integrator>
A system integrator headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri.
Parent company Barry-Wehmiller manufactures processing equipment.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Sometimes called batching.
A process to create products by using a set amount of raw materials at a time.
In between batches the product is meticulously tested for quality and safety and often the equipment is cleaned.
Equipment for batch processes is usually less expensive and not as automation dependent.
Different from:
Continuous Process
Engineering standard>
A standardized prefix for a unit of measure based on a power of ten.
The terms have been created recently by the IEC to end the confusion between a prefix describing an amount of
computer memory being a power of ten or a power of 2.
At smaller memory sizes the difference between the two was negligible and they were sloppily used interchangeably.
But, at current memory device sizes the difference is significant and will get larger as average sizes increase.
The term for power of ten prefixes is a Metric prefix.
See:
1. Electronic Bus. (for digital signal communications usage)
2. Electrical Bus. (for power transmission usage)
Business process>
A concept or activity that makes achieving profitability easier.
Business process>
A State of California license for an electrical contractor.
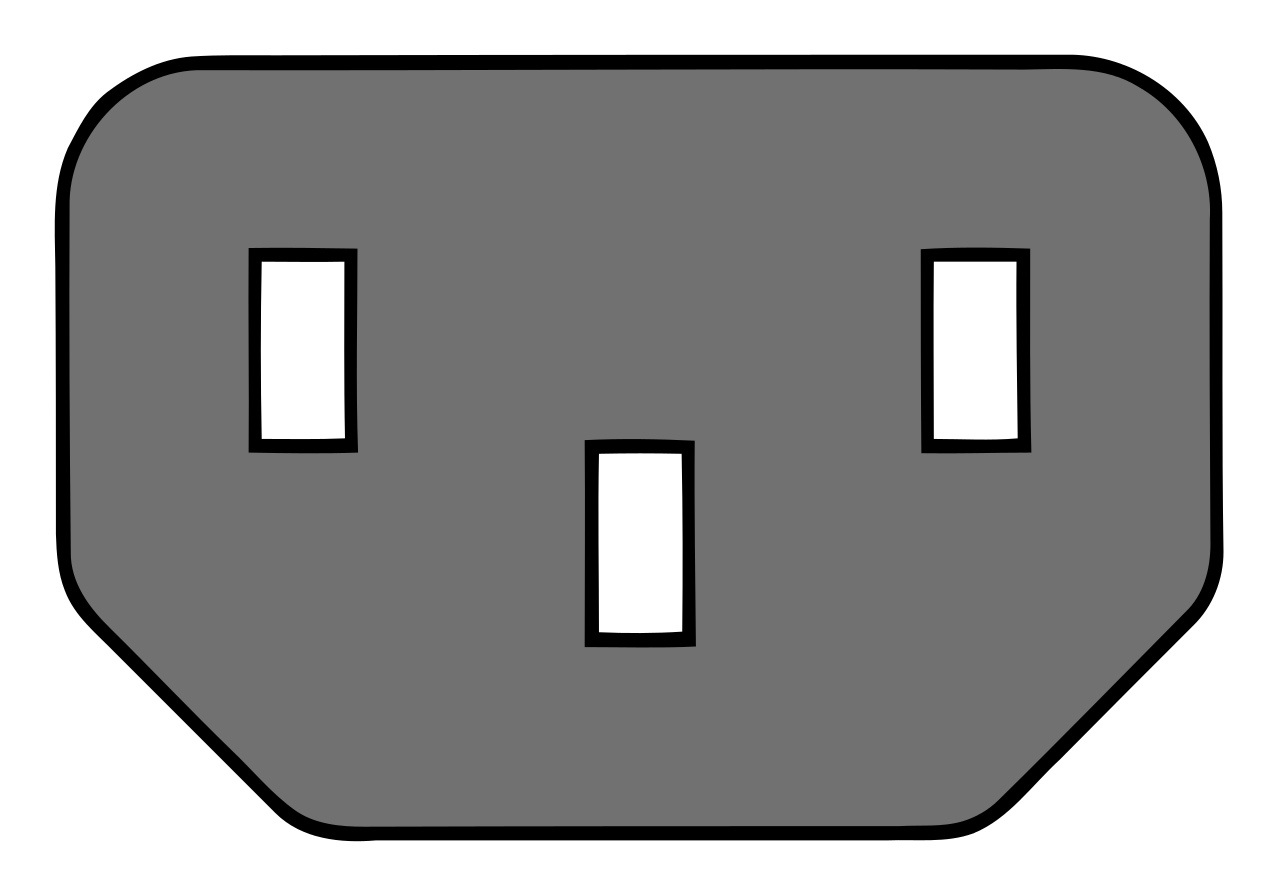 Hardware>
Connector>
Hardware>
Connector>
A power connector. The most common connector type of IEC 60320 series.
Found most often on computers and other electronic appliances.
Commonly just called an IEC connector because of their ubiquity
Hardware>
A collection of insulated electrical conductors.
The conductor is usually made of copper, sometimes aluminum.
The insulation is some kind of plastic, usually PVC.
Raw cable is supplied in spools usually, in lengths of 100, 200, 500 and 1000 feet.
Finished cables have connectors attached at the ends.
A cable harness is a number of finished cables bundled together in such a way to fit well inside a contol panel or machine.
See:
1. Client Access License. (for software usage)
2. Calibration. (for sensor usage)
Hardware>
Sensor>
Adjusting the output of a sensor so that it will as closely as possible match the definition of the parameter being measured.
Typically accomplished by using a reference standard traceable back to a national standards lab such as NIST in the USA.
Standards organization>
An organization in Canada that creates voluntary consensus standards for safety and interoperability of devices.
They produce the Canadian Electrical Code, CSA C22.1.
It is a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
Cisco>
A Cisco brand of network switch.
| Name | Construction | Speed | Length | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat 3 | UTP | 10 Mbit/s | 100 meters | 10BaseT |
| Cat 5e | UTP | 100 Mbit/s | 100 meters | 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet) 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet) 2.5GBASE-T 5GBASE-T |
| Cat 6 | UTP | 250 Mbit/s | 55 meters | 10GBASE-T |
| Cat 6A | UTP | 500 Mbit/s | 100 meters | 10GBASE-T |
| Cat 7 | STP | 600 Mbit/s | 100 meters | 10GBASE-T |
| Cat 8 | STP | 10 Gbit/s | 30 meters | not for structured cabling |
Computing>
An obsolete display technology based on a vacuum tube.
Replaced by LCD displays.
See Clean Dry Air.
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of temperature. Also sometimes called centigrade.
It is one of the derived units of the International System of Units.
The current ISO/IEC 80000 standard defines Celsius by means of a physical measurement only feasible in a calibration standards lab.
In practice each degree is one hundredth of the temperature between the freezing point of water (0°C)
and the boiling point of water (100°C) both at 1 atmosphere pressure.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 10-2 or a hundredth of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is c.
A typical usage would be centimeter.
Hardware>
Automation control>
A device that continuously plots the values of one or more parameters on a circular paper or strip paper roll or on an electronic screen.
Higher end models have built in control capabilities from as simple as closing a switch when a parameter exceeds a set value to
a full complex logic controller.
Since the electronic chart recorders already have a microprocessor to do the plotting function and plotting is a small task
compared to the available processing capabilities of low end modern processors, there is plenty space computing capacity in most models.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A non-flat metal shape that holds electrical or electronic components and provides structural support for them.
Often box like but not fully enclosing the components.
Usually placed inside another box that provide dust and moisture protection and safety from electric shock.
Similar to a Subplate.
See Clean In Place.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
An OEM of networking equipment.
Cisco is the dominant brand and their command line interface CLI is the default standard of configuring switches and routers.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Similar to:
Instrument air
Different from:
Shop air
Software>
A license for users to access Microsoft SQL Server.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
The lowest cost metal material for electrical enclosures.
Prone to rusting, so almost always powder coated.
Does not perform well in a wash-down sanitary environment.
Similar to:
Mild steel
System Integrator>
System Integration>
The integration step where a system integrator runs the new controls to determine any unforeseen problems. The step follows installation.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation line of PLCs.
Computing>
Using electronic devices to perform mathematical and logical operations.
Convergence has enabled computing devices to do graphical, symbolic, communications and other more complex operations.
Computing>
A display device showing a dialog with a computer. A display with no memory or processing capability for use with a computer.
Typically using LCD technology with LED backlighting.
Computing>
A older and less common name for a "computer monitor" or a Thin client.
Business process>
Giving a lot of information clearly and in a few words; brief but comprehensive.
What we aim for in every document provided to our customers.
One of the "much easier said than done" concepts in life.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A tube that encloses wire and/or cables as they are routed between control panels, junction boxes, switchgear and machines.
Often made of thin wall metal that can be bent into arcs that allow easy pulling of the wires through the conduit.
Sometimes made of plastic.
Metal conduit also acts as a shield for electrical noise.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
An open tray that holds wires and cables.
Usually of rectangular shape. Can have solid or mesh walls.
Different from a Conduit which is fully enclosed.
Hardware>
A mechanical connection in an electrical circuit that allows easy removal & insertion for quick assembly & troubleshooting.
Different from:
Hard wired
Hardware>
Connector>
A metal pin, socket, ferrule or lug at the end of a wire.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Clean In Place>
The time a cleaning solution is in contact and acting upon a surface.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A process to create products by feed raw materials steadily over time.
Appropriate sensors are needed to test fthe produst for quality and safety in real time.
Equipment for continuous processes are usually more expensive and are very automation dependent.
Different from:
Batch Process
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A current Rockwell Automation PLC product
Networking>
Network>
An open industrial network protocol for industrial automation applications, also known as a fieldbus.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A flat surface where devices to control a process are mounted.
Often the back of the panel is enclosed to protect the devices from harsh environments as well as protect human users from electrical shock.
Also, can be a computer monitor screen display that emulates a hardware panel.
| Company | Headquarters | Revenue | Employees |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASEA Brown Boveri (ABB) | Zürich, Switzerland | $28B (2019) | 145,000 |
| Eaton | Dublin, Ireland Beachwood, Ohio |
$18B (2020) | 92,000 |
| Emerson Electric | Ferguson, Missouri | $17B (2020) | 84,000 |
| General Electric | Boston, Massachusetts | $76B (2020) | 200,000 |
| Honeywell | Charlotte, North Carolina | $33B (2020) | 100,000 |
| LS Group | Anyang, South Korea | $25B (2010) | unreported |
| Mitsubishi Electric | Tokyo, Japan | $39B (2017) | 140,000 |
| Omron | Kyoto, Japan | $9B (2016) | 40,000 |
| Rockwell Automation | Milwaukee, Wisconsin | $7B (2019) | 23,000 |
| Schneider Electric | Rueil-Malmaison, France | $32B (2019) | 130,000 |
| Siemens | Munich, Germany | $68B (2020) | 295,000 |
| Yokogawa Electric | Tokyo, Japan | $4B (2017) | 18,000 |
Hardware>
Actuator>
Valve>
A valve designed and used for adjusting (throttling) the amount of material flowing through it.
Typically not used to turn on and off flows or isolate pipe sections.
See Control Panel.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A Indian English multiplier of 107 or ten million of the base unit.
It is written 1,00,00,000.
Often encountered when communicating with outsourcing partners.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
OEM of relays.
See Cold Rolled Steel.
See Cathode Ray Tube.
See:
1. Culture Tank.
2. Current Transformer.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A tank used to ferment dairy fluids into different desired products.
The tank is designed to promote bacterial growth and has the opposite function of a pasteurization tank.
Hardware>
Sensor>
Typically used in context of 3-15 psig transducer communications.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation local area network designed to support remote programming and
messaging between computers and controllers for factory-floor applications.
Abbreviated as “DH+”.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
The seventh and highest layer of the OSI Model of networking.
It deals with communications between two network devices over a physical link.
System Integrator>
System Integration>
Expedited or emergency service provided outside of the normal scheduling process and requiring the service provider to drop something or drop everything to serve the customer.
Similar to:
Standard service
See:
1. Demolish.
2. Demonstrate.
Standards organization>
In English: German Institute for Standardization.
It represents all German standards creating bodies at ISO.
It also creates its own standards, many of which are commonly used in America.
Key DIN standards are:
DIN 43700 for the cutout sizes for panel mounted instruments (now replaced by DIN/IEC 61554)
IEC/EN 60715 for metal rails inside enclosures to snap components into.
See Data Highway Plus.
See Digital Input.
Hardware>
Sensor>
A circuit that accepts a digital signal from a sensor or switch and
adjusts the output voltage level to be compatible with the control system.
This is usually between 0 to 0.8 VDC meaning off, low or zero and between 2 to 5 VDC meaning on, high or one and often called TTL level.
The input circuit is designed to accommodate a specific input range of voltages and currents.
The circuit also uses a filter to remove electrical noise from the world outside of the control system.
Typically the input and output portions of the circuit are isolated electrically isolated from each other by converting the signal to a optical one
and then back to an electrical one. This prevents most overloads from the outside world from affecting the control system.
Many unit also have an indicator LED to show the state of the input for troubleshooting.
Similar to:
Analog Input
Analog Output
Digital Output
Hardware>
Sensor>
A circuit that accepts a digital signal from the control system and converts it into a digital signal
at a different level of voltage and current to drive an output device.
Typically the input and output portions of the circuit are isolated electrically isolated from each other by converting the signal to a optical one
and then back to an electrical one. This prevents most overloads from the outside world from affecting the control system.
Many unit also have an indicator LED to show the state of the output for troubleshooting.
Similar to:
Analog Input
Analog Output
Digital Input
Networking>
Network>
A method of external Internet connection using copper wire, usually existing telephone wire.
Networking>
Network Device>
A rack for networking & telecommunications wiring, network switches and servers in a building.
The best designs focus on neat easy to maintain wiring as well as enclosures that protect the contents from the harsh industrial environment.
Since around three quarters of all network failures occur at the physical level,
neat & orderly cable management and dust & electrical noise protected frames are key to a reliable network.
See Hardening Layer One.
The name is used for both a rack and a room (closet) of one or more such racks.
In a large network system, multiple IDFs for different locations or floors are connected to a central Main Distribution Frame MDF for the building.
See Digital Output.
Hardware>
Connector>
A connector with a D-shaped shell. The most well known being the DB-25 connector for serial ports.
The shell has a rounded trapezoid shape which most looks like the Latin capital letter D.
The shell and the asymmetric organization of the pins causes the connector to be oriented in only one possible way thus preventing an incorrect connection.
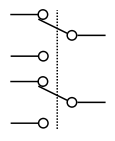 Hardware>
Switch>
Hardware>
Switch>
A configuration of an electrical switch where the mechanical actuator controls two electrically isolated SPDT switches.
Similar to:
SPST
SPDT
DPST
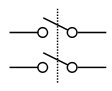 Hardware>
Switch>
Hardware>
Switch>
A configuration of an electrical switch where the mechanical actuator controls two electrically isolated SPST switches.
Similar to:
SPST
SPDT
DPST
Computing>
A hard disk with two independent read/write interfaces to the controller for redundancy.
Software>
A URL embedded in a piece of text that allows access to another web page with more or different information.
Software>
Human Machine Interface>
The indication on an HMI of the real-time condition of a component (on or off, empty or full)
See Voltage to Pneumatic.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
OEM of electric power distribution & management products.
Incorporates the assets of some well known brands: Westinghouse Distribution and Controls, Cutler-Hammer, Pulizzi,
Aeroquip, Arrow Hart, Cooper, Crouse-Hinds, Bussmann, B-Line, Ronningen-Petter filters & Vickers.
Hardware>
Motor control>
A set of electrical power conductors that distribute power to loads. The conductors are often in metal bar form (copper or aluminum),
but sometimes in cable form.
Hardware>
Connector>
A set of electrical conductors in parallel that allow digital communication between two or more devices connected to the conductors.
Typically, a bus has signal carried in parallel and a network has signals carried in series.
However, modern technology has blurred that distinction with many exceptions and hybrid architectures.
Standards organization>
A trade association that creates voluntary consensus standards for interconnect, passive and electro-mechanical electronic components.
It does not do any product testing.
The organization has had many names before (such as RETMA & Electronic Industries Association) and continues to keep changing its naming and structure.
EIA standards originally were prefixed with RS which stood for Recommended Standard.
Well known original standards are:
RS-232 for serial communications
RS-274 for numerical control coding for machine tool paths (also known as G-code or Gerber)
RS-279 for the color band coding for resistors
RS-422 for serial communications
RS-485 for serial communications
Electronics>
Circuits of components that modify the flow of electricity to achieve amplification, computation, filtration, rectification, switching and/or conversion.
Hardware>
Switch>
A safety control that should be accessible to anybody to use but that also should have physical guards to prevent accidental triggering.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
OEM of automation solutions. Incorporates the assets of some well known brands: Rosemount, Asco (red hat valves), Fisher valves & Sola.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation enhanced version of their Ethernet Bridge module
Hardware>
A metal (steel or stainless steel) or plastic (fiberglass or polycarbonate) box that supports and protects the control components
from the industrial environment. It also protects humans from contact with electricity when properly closed.
Engineering standard>
Documents that specify standard ways to design certain aspects of a system.
Standards can be unique to a corporation, nationwide, or international.
Standardization typically accomplished uniformity, interoperability and economies of scale.
Standard symbols and layouts on schematics and operator interfaces used across a company or in an industry reduce training times and
allow a greater pool of qualified workforce labor.
Hardware>
Automation control>
The process of manually matching IO points to the equipment, device, location, sensor, and/or function.
The IO wire lines coming into a control box are unable to be distinguished from one another without outside specification.
Unlike networked devices that can self-identify themselves, most IO lines cannot do that.
See:
1. Emergency Shut Down.
2. Electro-Static Discharge.
See Emergency stop.
Engineering standard>
Binary prefix>
A multiplier of 260 of the base unit.
A typical usage would be for memory as in a ExbiByte or EiB.
An Exbi quantity is about 15.3% larger than a decimal Exa 1018 quantity.
Thus, an ExbiByte is approximately 15.3% larger than an ExaByte.
Because this term in new and more precise in its meaning, it will take a while to catch on.
When comparing memory capacity of devices in a quotation, it is important that the units are clarified.
It is unlikely that one will get 15% more of something for the same price.
Software>
Human Machine Interface>
A graphical way for a DCS to replicate the front panel controls and indicators of a panel instrument on a HMI.
Standards organization>
The company employs a non-traditional business model whereby risk and premiums are determined by engineering analysis
as opposed to historically based actuarial calculations.
This business approach is centered on the belief that property losses can be prevented or mitigated.
FM engineering personnel regularly visit insured locations to evaluate hazards and recommend improvements to their property or work practices to
reduce physical and financial risks if a loss occurs.
FM creates standards based on testing in fire, explosion, and hazards detection.
It is a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
Rockwell Automation’s SCADA software product.
Computing>
A regular PC with a local hard drive where data can be stored.
Hardware>
Connector>
A tubular metal terminal applied to the end of stranded wire that contains the strands and allows easy connection to a terminal block.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
A German OEM of pneumatic components and innovative experimental robotics.
See:
1. Fiber optic cable.
2. Fiber optic communication.
Networking>
Network>
A method of external Internet connection using fiber optic cables.
Hardware>
Connector>
A connection to a device not inside a control panel. Likely to be at a junction box.
Hardware>
Automation control>
A sensor or actuator device not inside a control panel.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A device to remove undesired particles from a fluid.
Software>
Log>
Reducing the amount of data in a log to gather pertinent information to an inquiry or investigation.
See Full Load Amperes.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation generation of IO products, sometimes called 1794.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A current Rockwell Automation I/O product.
See Free On Board.
Business process>
The point at which a seller (like your system integrator) is no longer responsible for shipping cost.
See Factory Talk View.
Hardware>
Motor control>
A form of motor starter.
See General Electric.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
A 125 year old OEM with an impressive record of technical accomplishment and market leadership in many areas.
Automation products are now mostly software and provided by the GE Digital division based in San Ramon, California.
Engineering standard>
Binary prefix>
A multiplier of 230 of the base unit.
A typical usage would be for memory as in a GibiByte or GiB.
An Gibi quantity is about 7.4% larger than a decimal Giga 109 quantity.
Thus, a GibiByte is approximately 7.4% larger than a GigaByte.
Because this term in new and more precise in its meaning, it will take a while to catch on.
When comparing memory capacity of devices in a quotation, it is important that the units are clarified.
It is unlikely that one will get 7% more of something for the same price.
This prefix may also start to be used in a data rate setting as in GibiBytes per second.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 109 or billion of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is G.
A typical usage would be GigaHertz.
System Integrator>
A system integrator headquartered in Oak Brook, Illinois.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
Physical Layer>
A design strategy to improve reliability and increase OEE by making the physical infrastructure the network is built upon as robust and protected as possible.
Electronics>
for either human or machine safety or both.
Hardware>
Connector>
An electrical cable connected to a terminal without an easily removable and replaceable connector.
The connection could be through a screw terminal, a wire nut where the strands of two or more wires are twisted together,
a wire clamp, or a permanent soldered joint.
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of electrical frequency.
It is one of the derived units of the International System of Units.
The ISO/IEC 80000 standard defines a Hertz as a cycle per second.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A sweetener ingredient.
Hardware>
Switch>
Whether a device acts as the controller (host) or passes the data and control from another controller (remote).
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
The unit of measure typically used to size motors and motor protection & control devices.
See:
1. Horsepower.
2. Hewlett-Packard.
Networking>
Network Device>
An obsolete device that connects many networked devices.
Replaced by a network switch with much better performance and security at approximately the same cost.
See Input Output.
See Current to Pneumatic.
Hardware>
Connector>
A standard for circular pin and sleeve electrical connectors.
Each version is color coded and keyed to indicate voltage range and conductor phase configuration.
Hardware>
Connector>
A standard for household electrical appliance connectors.
The most common version is C-13 for computers.
Each version is indicated with C followed by a number.
The male plugs are odd numbers and the female sockets they plug into are the next even number.
Each version is distinguished by shape and size are available for different current, temperature and earthing requirements.
However, unlike IEC 60309 connectors, they do not have a specified operating voltage.
Engineering standard>
A globally accepted scheme of certification to voluntary consensus standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
relating to equipment for use in Explosive atmospheres. Hence "IEC Ex".
Not to be confused with ATEX which is European law, but both achieve the same ends.
A General Electric SCADA software product. Formerly created by Intellution which was acquired by GE.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
Inductive Automation>
An Inductive Automation SCADA software product.
Electronics>
A method of testing printed circuit boards using a bed of nails to access test points inside the circuit board.
By being able to access the internal junctions of the circuit, it can thoroughly test small portions of the circuit for individual functionality.
If all internal circuit sections work it can be assumed the the entire circuit board will work as a whole.
This is opposite of a functional test which uses the normal connectors to the board as the sole access points and
tests how the entire board performs its function without testing individual circuit sections and components separately.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
An OEM of SCADA software products.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A box containing PLC’s, HMI’s, VFD’s, power supplies, terminal blocks, relays, and other electrical automation devices wired together
to perform the functions required.
It is fully enclosed to protect the devices from harsh environments as well as protect human users from electrical shock.
The front of the enclosure is a flat surface where pilot devices to indicate and control a process are mounted.
Networking>
Network Device>
Distribution Frame>
A network Distribution Frame that serves a portion or all of the industrial production area in a building,
structure or vessel.
It and other Intermediate Distribution Frames will be connected to
a Main Distribution Frame.
Because it is located in an industrial area it will need to be better protected than if it was in an office environment.
Business process>
Technologies that have created the computer-centric lifestyle based on the convergence and eventual unification of
telephones, computers, audiovisual, mail, forms, documents, education, entertainment, radio and television.
The term reflects the realization that IT has become more that what it traditionally was, and that the IT department
will need to improve their skills, performance, and quality to meet the demands of the new workplace lifestyle.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
The process of keeping dust & moisture from entering an electrical enclosure.
A set of protection levels for electrical enclosures defined by IEC standard 60529.
See also NEMA enclosure type.
Software>
A command not allowed to happen by the control system because of one or more process rules being enforced.
Hardware>
Sensor>
Applies to either digital or analog signals.
System Integrator>
System Integration>
The integration step where a system integrator adds new controls to a process.
The step should be preceded by the simulation and testing of the control software offsite.
The step will be followed by commissioning.
Standards organization>
A technical society that creates voluntary consensus standards for electric power, networking, IoT & cyber security.
It does not do any product testing.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
An extremely clean supply of compressed air that is free from contaminates such as moisture, oils & particulates.
Instrument air is important to use for valves & pneumatic controls as they have very precise sliding seal surfaces that can be easily damaged or corroded by impure air.
Software>
A data type for numbers that whole and do not have decimal points.
This is opposite of floating or real numbers which do have decimal points.
Business process>
Knowledge & documentation as a business asset worth protecting and using for financial gain.
See:
1. Hardware Interlock
2. Software Interlock
Networking>
Network Device>
Distribution Frame>
A network distribution frame that serves a portion of a building, structure or vessel.
One or more IDF's are connected to the Main Distribution Frame (MDF).
Standards organization>
A Geneva, Switzerland based organization with worldwide representation that creates of voluntary consensus standards relating to electricity.
IEC standard methods are slowly replacing the pioneering but only American centered NEMA standards.
Standards organization>
The umbrella organization for coordinating and harmonizing standards across nations.
Each of 167 nations is represented at ISO by one standards body.
For the United States, the representative organization is the American National Standards Institute.
ISO does not do any product testing.
Standards organization>
A technical society that creates voluntary consensus standards for instrumentation, automation & cyber security.
ISA does product testing limited to cybersecurity certification to ISA/IEC 62443 standards and
compliance for wireless sensors and infrastructure devices to the ISA100.11a-2011 (IEC 62734) standard.
ISA also provides professional certifications in Automation, Control Systems Technician, Automation Project Management,
Cybersecurity, and Safety Instrumented Systems.
A standard for a rational system of units rather than a customary one. It is defined in ISO/IEC 80000 and is revised around every decade. It is built on a foundation of seven base units with all other units being derived from the base units. It is created from logic and knowledge of physics rather than using unrelated arbitrary units passed down from history. The seven base units are: second, meter, kilogram, Ampere, Kelvin, mol, candela. The derived units most commonly found in system integrator quotes are: degree Celsius, Hertz, Newton, Ohm, Pascal, Volt, and Watt.
Networking>
Network>
The principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries.
Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
AVEVA>
AVEVA HMI software product. Formerly known as Wonderware InTouch.
Hardware>
Motor control>
A class of motors that have better heat dissipation, thicker insulation and higher resistance to voltage spikes so
that they can be successfully run using a Variable Frequency Drive and get the expected motor lifetime.
See Input Output.
See:
1. Internet Protocol.
2. Ingress Protection.
3. Intellectual Property.
Standards organization>
Formerly the Institute of Printed Circuits. Now just IPC.
A trade association that creates voluntary consensus standards for the assembly and production of electronic equipment and assemblies.
IPC does not do any product testing.
IPC does provide professional certifications to their standards.
Engineering standard>
An IPC workmanship standard for printed circuit boards.
Any circuit board inside a power supply, PLC, VFD, network switch, sensor, transmitter, etc. should be made to this standard.
Engineering standard>
An IPC workmanship standard for electrical cable & wire harness assemblies.
Used by system integrators for the internal wiring of control panels and for the external cables that go from
control panels to the sensors and actuators in the plant.
See:
1. Instrument Society of America. (original name)
2. International Society of Automation. (current name)
An Emerson Electric brand (formerly Control Concepts) of surge protectors.
See Junction box.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
An electrical enclosure (usually small) that only contains wire connections (often using terminal blocks) and no control devices.
Computing>
The essential peripherals for a human to interface to a computer.
However, the computer does not need to have these peripherals to do its work.
Thus, a human can interface with many different computers with a single keyboard video & mouse set.
Engineering standard>
Binary prefix>
A multiplier of 210 of the base unit.
A typical usage would be for memory as in a KibiByte or KiB.
An Kibi quantity is about 2.4% larger than a decimal Kilo 103 quantity.
Thus, a KibiByte is approximately 2.4% larger than a KiloByte.
When comparing memory capacity of devices in a quotation, it is unlikely that the difference between these prefixes will make much difference.
Most memory is produced in sizes much larger than this range.
Because this term in new and more precise in its meaning, it will take a while to catch on.
This prefix may start to be used in a data rate setting as in KibiBytes per second.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 103 or thousand of the base unit.
Its official abbreviation is k but often also K.
A typical usage would be KiloHertz, kilometer, KiloVilt, KiloWatt or KiloWatt Hour.
Computing>
Keyboard Video & Mouse>
A device that allows the Keyboard Video & Mouse to be located remotely (like in a control room) from the computer they control and interface to.
Because the maximum length of cable for these 3 devices is limited,
the KVM extender often includes some form of signal amplification and maybe even some noise filtering.
Computing>
Keyboard Video & Mouse>
An electromechanical or electronic switch that allows a single keyboard video & mouse set to interface/control two or more computers.
Works the same as unplugging one computer and plugging in another except with the flick of a switch.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
Legacy processor for Rockwell Automation PLCs
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
Processor for Rockwell Automation PLCs
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A Indian English multiplier of 105 or hundred thousand of the base unit.
It is written 1,00,000.
Often encountered when communicating with outsourcing partners.
See Local Area Network.
See Light Emmiting Diode.
Electronics>
A semiconductor source of light that can be used in different ways:
1. As a single spot indicator light or an array of such spots (example: seven segment display)
2. As the source of back lighting for an LCD display.
3. As a general illumination technology that more efficiently replaces incandescent & fluorescent lighting.
Hardware>
Motor control>
Applied to VFD’s.
Hardware>
Switch>
Whether a device is controlled by the front panel controls (local) or by controls located at another panel or computer (remote).
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation generation of IO products, sometimes called 1756.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
Korean manufacturer of a full line of electrification apparatus. Also has a copper smelting division that allows
LS to be very competitive in copper based products like wire, cable, bus bars and substation equipment. Has only
recently operated in the North American market so market share is small.
See Level Switch High.
See Level Switch Low.
See Level Switch Low-Low.
See milliAmpere.
See Media Access Control.
Hardware>
Switch>
An electromechanical device that makes of interrupts electrical connection in a circuit by human actuation.
System Integrator>
A system integrator headquartered in Tampa, Florida.
Parent company Rockwell Automation manufactures controls equipment.
See Motor Control Center.
Engineering standard>
Binary prefix>
A multiplier of 220 of the base unit.
A typical usage would be for memory as in a MebiByte or MiB.
An Mebi quantity is about 4.9% larger than a decimal Mega 106 quantity.
Thus, a MebiByte is approximately 4.9% larger than a MegaByte.
When comparing memory capacity of devices in a quotation, it is unlikely that the difference between these prefixes will make much difference.
Memory capacity at this small a quantity is usually very inexpensive and now typically produced in much larger sizes.
Because this term in new and more precise in its meaning, it will take a while to catch on.
This prefix may start to be used in a data rate setting as in MebiBytes per second.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 106 or million of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is M.
A typical usage would be MegaHertz or MegaWatt.
Electronics>
Typically CMOS - Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor.
The dominant process for making integrated circuits.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A standardized prefix for a unit of measure based on a power of ten.
The term for power of two prefixes is a Binary prefix.
See Manual Off Switch.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
The lowest cost metal material for electrical enclosures.
Prone to rusting, so almost always powder coated.
Does not perform well in a wash-down sanitary environment.
Similar to:
CRS
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 10-6 or millionth of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is μ.
Typical usages would be micrometer (also called a micron), microsecond, or microFarad (electric capacitance).
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 10-3 or thousandth of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is m.
Typical usages would be millimeter, millisecond, milliVolt, MilliAmp or MilliWatt.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
Japanese conglomerate with a factory automation division. Offers a full line of PLCs, HMIs,
VFDs, low voltage and medium voltage switchgear, robots, machine vision, and some
specialized CNC equipment. Has a sister division that makes digital and power semiconductors
that enables competitive solid state power control applications.
See Manual – Off – Auto.
Business process>
Also called reference model or conceptual model.
A simplified way of looking at the complexiity of reality to make it more understandable.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
A Schneider Electric brand of PLC products.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
Modicon>
Current generation of Schneider Electric PLC’s.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
Modicon>
A legacy generation of Schneider Electric PLC’s.
See:
1. Process monitor.
2. Computer monitor.
See Mix-proof valve.
1. Not Applicable.
2. North America.
1. Not Applicable.
2. North America.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 10-9 or billionth of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is n.
Typical usages would be nanometer, nanosecond, or nanoFarad (electric capacitance).
Dimensions for atomic distances, wavelengths of light and of semiconductor integrated circuit features are of expressed in nanometers.
Engineering standard>
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standard 70.
It has been adopted as law by most American municipalities for governing how electrical wiring should be done in buildings.
State licensed electricians, such as a California C10, are trained and tested on the National Electric Code.
The National Electric Code also specifies that all electrical devices used must be tested and "listed" by
a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory.
This is especially of concern for industrial control panels for equipment or custom made for a process plant.
Such panels must be assembled by a UL 508 panel shop using UL listed enclosures, wire and components.
Standards organization>
An organization in the US that creates voluntary consensus codes and standards for fire safety.
Their best known standard is NFPA 70 the National Electric Code.
It does not do any testing.
Standards organization>
Occupational Safety and Health Administration>
A third-party organization that has the necessary qualifications to perform safety testing and certification of products as
recognized by OSHA.
The EU equivalent of an NRTL is a Notified Body.
To avoid any conflict of interest, a third-party organization is always preferred over in-house testing only.
Standards organization>
An organization in the US that creates voluntary consensus codes and standards for public health and safety.
It specializes in food equipment, anything that will come in contact with drinking water, health sciences equipment, and consumer product that contact food.
It is a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory.
See:
1. Normally Closed.
2. Numerical Control.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
An electrical enclosure rated to protect against blowing dust but only dripping and light splashing water. Not suitable for applications where equipment is being washed down for sanitary reasons.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
An electrical enclosure rated to protect against dust and hose directed water.
Networking>
Typically an Ethernet communications network using Internet Protocol.
But other architectures of networks are possible and still common.
Several (mostly legacy) fieldbus networks were/are used to handle lower level networking because they are less expensive.
As the cost of Ethernet based devices keep dropping, the viability of non-Ethernet fieldbuses gets less over time.
Networking>
A physical object that can connect to a network and communicate with other devices on the network.
Networking>
The technology of passing digital data from one computer to another using serial communications
where the destination is controlled by an address rather than a unique physical connection.
Networking>
Network Device>
A network component that connects various Ethernet devices.
See:
1. Network Interface Controller.
2. Network Interface Card.
Networking>
Network Device>
The physical device that connects a computer to a network.
Usually the place where the specific MAC address for the computer is permanently stored.
Networking>
Network Device>
Network Interface Card>
The processor located on the Network Interface Card that manages the communications across the physical layer media.
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of mechanical force.
It is one of the derived units of the International System of Units.
The ISO/IEC 80000 standard defines a Newton as a kilogram meter per second squared.
See Normally Open.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A mechanical cable that opens and closes a circuit breaker from outside of the enclosure.
Allows a cabinet to be de-energized before it is opened for safety purposes.
Hardware>
Connector>
A series of North American power cord connectors specified by NEMA that come in locking and non-locking versions.
Standards organization>
An agency of the United States Department of Labor that administers the
Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) program.
Hardware>
Connector>
Classic connector for relays that originated with vacuum tube technology.
Has very rugged pins that are hard to bend or break.
A robust packaging design that has stood the test of time, but is a bit bulky for some applications.
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of electrical resistance.
It is one of the derived units of the International System of Units.
The ISO/IEC 80000 standard defines an Ohm as a kilogram*meter/second3*Ampere2.
However, this is better understood as a Volt/Ampere as it is another expression of Ohm's law where
Voltage equals Current time Resistance (V=IR).
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
A Japanese electrical equipment manufacturer that has an industrial automation division that makes
PLC's, HMI's machine vision and sensors, as well as a components division the makes relays & switches.
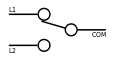 Hardware>
Switch>
Hardware>
Switch>
A configuration of an electrical switch. Also called an SPDT or a 1PDT.
Networking> A conceptual model created by the Open Systems Interconnection working group of the ISO used to organize and facilitate understand of the complexities of networking. There is slightly different simplified version of the model called the Internet Protocol Suite.
See Pneumatic to current.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
An OEM of cable management and wire termination (lugs & ferrules) products.
Best known for plastic channel with fingers that holds wires together in a control panel.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A flat piece of material to mount indicating and controlling devices.
Either used inside a fully enclosed box for safety and protection or as the front of the box to allow operation interaction.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A brand of HMI from Rockwell Automation.
Engineering standard>
Unit of Measure>
A unit of mechanical pressure.
It is one of the derived units of the International System of Units.
The ISO/IEC 80000 standard defines a Pascal as a kilogram/meter*second2.
But this is not as intuitive as force per area as in Newton per square meter.
This matches the format for mechanical pressure in convention units which is pounds per square inch.
A Pascal is a very small unit. 1 psi is about 6895 Pascals. Thus, often pressure is expressed in kiloPascals kPa or even megaPascals mPa.
A Pascal is about one thousandth of atmospheric pressure at sea level.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A tank used to keep fluid products that have already been pasteurized.
The tank is designed to prevent bacterial growth and has the opposite function of a fermentation or culture tank.
Engineering standard>
A regulation from the US FDA first created in 1924.
It is updated regularly to keep up with developments in microbiological science & dairy technology.
Latest version is from 2017
See PushButton.
See Personal Computer.
Engineering standard>
Binary prefix>
A multiplier of 250 of the base unit.
A typical usage would be for memory as in a PebiByte or PiB.
An Pebi quantity is about 12.6% larger than a decimal Peta 1015 quantity.
Thus, a PebiByte is approximately 12.6% larger than a PetaByte.
Because this term in new and more precise in its meaning, it will take a while to catch on.
When comparing memory capacity of devices in a quotation, it is important that the units are clarified.
It is unlikely that one will get 12% more of something for the same price.
Computing>
A general-purpose computer used by a single person to perform personal productivity tasks.
Different from a server which is used indirectly by many users and connected to the users through a network.
Also different from a thin client device as a PC has internal file storage and hosts most of the applications it runs.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 10-12 or trillionth of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is p.
A typical usage would be picoFarad (electric capacitance).
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A detailed diagram in the process industry which shows the piping and process equipment together with the instrumentation and control devices.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation generation of IO products, sometimes called 1771.
See:
1. Program Management Office.
2. Pasteurized Milk Ordinance.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
A brand of plastic air tube used for controlling valves.
Electronics>
An electronic device that converts AC power to DC power and regulates it at one or more specific voltages.
used to provide control voltages for most of the devices in a control panel.
Constructed of one or more printed circuit boards in a protective metal or plastic enclosure.
Computers, PLC's, Network switches & routers have their own power supplies.
Most of the time the power supply PCB is separate from the device's main PCB for reasons of heat & electrical noise separation.
Sometimes, when space is at a premium, the power supply circuit is one the same PCB as the PLC.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation brand of VFD’s
Engineering standard>
A logically determined series of standard integral sizes for dimensions or ratings of components that follow a roughly logarithmic scale.
In the context of control systems, it determines the most common Amperage ratings of circuit breakers, fuses, motors and VFD’s.
Also known as Renard numbers or IEC E-series number.
System Integrator>
A system integrator headquartered in Smyrna, Tennessee. Also uses the name Entegrasys.
Electronics>
The substrate on which is mounted the electronic components used in power supplies, PLC's, HMI's, servers, VFD's, sensors, network switches and other devices.
A PCB is rarely found inside a control panel without its own plastic or metal enclosure.
Dust and heat are the main causes of electronics failures.
As such, it is important to have all electronic devices protected inside temperature controled industrial enclosures.
Unprotected electronics in an industrial environment will fail prematurely and often at the most inopportune time for production.
Software>
The process of periodically polling the status of a process to determine its state and test for any error conditions.
This could be a physical or chemical process or a program running on a computer which is also called a process.
See:
1. Proximity switch.
2. Proximity sensor.
Hardware>
Sensor>
An analog output based on how far away (distance) from a target the sensor is.
Hardware>
Switch>
A digital on-off output based on how far away (distance) from a target the sensor is.
The switch changes state when the distance passes a certain threshold.
Proximity switches are commonly used to detect the presence of a pipe in a swing panel.
By using such switches the correct piping connections can be more assured and fluid routing mistakes prevented.
See:
1. Pasteurization Tank.
2. Potential Transformer.
Networking> The connection of Ethernet category cable using permanent insulation displacement terminals for individual wires instead of removable 8-wire RJ-45 connectors.
See Quality Assurance.
See Quality Control.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
A legacy generation of Schneider Electric field I/O products.
Hardware>
Connector>
A connector location on a backplane, especially that of a Programmable Logic Controller.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
Remote Administration.
An OEM & brand of remote support software that allows engineers at your system integrator to troubleshoot servers and PCs remotely,
thus providing faster and lower cost service to their customers.
Engineering standard>
EIA original produced what they called recommended standards.
The names of their earlier standards thus started with RS.
Today all standards are recommended being that they are voluntary to be followed.
Hardware>
Switch>
An electrically operated switch where there is no electrical connection between the circuit that controls the relay and the circuits that the relay controls.
See
See Remote Input Output.
Hardware>
Connector>
Common name for a modular 8-pin jack used for Ethernet cables in networks.
The version used for modern Ethernet cables should be formally called an 8P8C connector.
RJ is for Registered Jack and originated with the Bell System.
See Reverse Osmosis.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
Also known by their brand and previous company name Allen-Bradley.
See:
1. Requirements Specification.
2. Recommended Standard.
Engineering standard>
A serial communication interface.
See:
1. Resistance Temperature Detector.
2. Ready To Drink.
See Site Acceptance Test.
Software>
A US Department of Energy - Idaho National Labs free software used to
discover human performance trending insights and comparison among plant operator shifts, and plant sites.
Will require third party consultants to use optimally.
 Controls regime>
Controls regime>
A Paris based
See Schneider Electric.
Hardware>
Switch>
An electromechanical device that makes of interrupts electrical connection in a circuit by a physical action.
Examples: limit switch, level switch, pressure switch, proximity switch.
Computing>
A dedicated computer attached to the network that performs a specific task that serves many users through their personal computing devices and HMI’s.
Servers use rugged hardware and different operating systems to support their intensive tasks to manage, store, send and process data 24-hours a day.
In the controls arena servers are used to host SCADA, historian, business intelligence and management programs.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Also known as plant air or service air.
Pressurized air from a central compressor system.
Because of the long runs of pipe throughout the plant there is usually some condensed liquid water present in the air unless a specific dryer system is included. Also, most probably has some particles and oil in the air.
See:
1. System Integrator.
2. International System of Units. (Système International d’Unités in French)
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
A tank, usually cylindrical and tall used to store bulk fluids or granular solids.
Networking>
Network>
Internet Protocol>
OSI Model>
Applications Layer>
An Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and
for modifying that information to change device behavior.
System Integrator>
System Integration>
The integration step where a system integrator creates new controls to a process and runs them offsite
to make sure they are bug-free before installation at the customer site.
 Hardware>
Switch>
Hardware>
Switch>
A configuration of an electrical switch.
Similar to:
SPST
DPST
DPDT
 Hardware>
Switch>
Hardware>
Switch>
A configuration of an electrical switch.
Same as:
1PST
Similar to:
SPDT
DPST
DPDT
See Sterilize In Place.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A Rockwell Automation generation of IO products, sometimes called 1746
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A style of enclosure that prevents the inevitable pooling of water and the dishing that occurs with a flat top enclosure,
especially if anybody has stepped on or put something heavy on the roof.
Also provide extra surface area and volume for hot air to go and keep away from the control electronics.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
A Japanese OEM of fluid handing fittings & components. Name was formerly Shoketsu Kinzoku Kogyo which translates into English as Sintered Metal Corporation.
Computing>
although often regarding safety, not always
Hardware>
Actuator>
A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by way of an electromagnet.
Usually used to open a valve against a spring that holds it closed.
Computing>
A server-based report generating software system from Microsoft.
It is part of a suite of Microsoft SQL Server services that includes:
SSAS - SQL Server Analysis Services
SSIS - SQL Server Integration Services.
See Stainless Steel.
See Secure Sockets Layer.
See Stainless STeel.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A steel alloy with nickel and chromium that has high resistance to corrosion.
Best choice of enclosure material for outdoor locations and sanitary wash-down environments.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Hard piped air lines made of stainless steel, more rugged and cleaner than plastic air lines.
System Integrator>
System Integration>
Normal scheduling of service by a system integrator or maintenance provider that does not disrupt work being performed for other customers or projects.
This is opposite from Demand service.
Standards organization>
A group of technical experts that develop voluntary consensus standards.
Engineering standard>
A value for temperature and pressure that is most commonly found in a laboratory so that different sensors and processes can be compared easily.
The most common values are a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius (approximately room temperature)and a pressure of 100 kiloPascals (kPa) or one bar.
The pressure happens to be the average atmospheric pressure at around 360 feet above sea level.
That altitude happens to be on average closest to where most laboratories as located.
The convenience of the values is completely intentional.
Unfortunately, various industries and organizations around the world have chosen their STP to be close but not exactly the same.
As such, it is still always best to make sure STP is explicitly specified when selecting and calibrating sensors.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
sometimes called Steam In Place
See:
1. Shielded Twisted Pair.
2. Standard Temperature & Pressure.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A brand of Rockwell Automation unmanaged network switches.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A brand of Rockwell Automation managed industrial network switches.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
A brand of Rockwell Automation managed network switches.
Engineering standard>
The de facto open and standard method of managing and querying a database.
Not a super intuitive language, but with a large pool of highly trained programmers and a long history of stability and functionality
it has remained the default for decades.
Controls regime>
Rockwell Automation>
Rockwell Automation programming software for their ControlLogix line of PLC’s.
Hardware>
Enclosure>
A flat panel mounted inside an enclosure to allow the attachment of devices using fasteners that penetrate through the sub-panel but
not the enclosure back wall.
Often the sub-panel is populated and wired up before putting inside the enclosure.
This saves time in construction and the better visibility reduces errors.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
A Cleveland, Ohio OEM of stainless steel fluid handing fittings & components.
Their products are ultra reliable (no leaks) and their warranty covers both replacement of the product as well as the cost of replacing it.
See:
1. Network switch.
2. Manual switch.
3. Sensor switch.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
Crouzet Control>
Crouzet Control brand of time delay relays (now called SyrLine).
System Integrator>
The orderly process of implementing a change to manufacturing process.
System Integrator>
A company that designs, programs, documents and commissions the controls for a process.
Usually has a specialty in specific controls regimes & vertical markets.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
AVEVA>
An AVEVA SCADA software product. Formerly called Wonderware System Platform.
Hardware>
Automation control>
Data entered and stored in a higher level control device that identifies the IO point or device.
Also a name you assign to an IO address of a device or PLC.
It is also called “variable” or “symbol” depending on the manufacture of the device or PLC.
See:
1. ThermoCouple
2. TriCore
System Integrator>
TriCore>
TriCore’s employee badge card reader software product
System Integrator>
TriCore>
TriCore’s Flexible Clean computer program product for clean in place systems in the food, beverage, dairy, and pharmaceutical industry
System Integrator>
TriCore>
TriCore’s Flexible Track computer program product to track operations in food, beverage and dairy processing plants
Engineering standard>
Binary prefix>
A multiplier of 240 of the base unit.
A typical usage would be for memory as in a TebiByte or TiB.
An Tebi quantity is about 10% larger than a decimal Tera 1012 quantity.
Thus, a TebiByte is approximately 10% larger than a TeraByte.
Because this term in new and more precise in its meaning, it will take a while to catch on.
When comparing memory capacity of devices in a quotation, it is important that the units are clarified.
It is unlikely that one will get 10% more of something for the same price.
Standards organization>
A trade association that creates voluntary consensus standards for Information and Communication Technologies.
TIA does not do any individual product testing, but does test data centers for compliance to TIA-942.
It was formerly a part of the Electronic Industries Alliance.
Notable TIA standards encountered in the food industry are:
TIA-568 hierarchical cable system architecture & Category cable.
TIA-569 proper building design to support networks.
TIA-598 color coding for Fiber optic cable.
TIA-607 effective grounding for all network equipment to reduce electrical noise and increase safety.
SCS 9001 cyber/supply-chain security.
TIA should not be confused with CompTIA which is separate organization that focuses on training and certification of
Information and Communication Technologies professionals.
Engineering standard>
Metric prefix>
A multiplier of 1012 or trillion of the base unit.
Its abbreviation is T.
A typical usage would be TeraHertz.
See:
1. Connector terminal.
2. Computer terminal.
Computing>
A computer that runs from resources stored on a central server instead of a localized hard drive.
Thin clients work by connecting remotely to a server-based computing environment where most applications, sensitive data, and memory, are stored.
Thin client deployment is more cost effective than deploying regular PCs.
Because so much is centralized at the server-side, thin client computing can reduce IT support and licensing costs.
Security can be improved through employing thin clients because the thin client itself is restricted by the server.
Thin clients cannot run unauthorized software, and data cannot be copied or saved anywhere except for the server.
System monitoring and management is easier based on the centralized server location.
Thin clients can also be simpler to manage, since upgrades, security policies, and more can be managed in the data center instead of on the endpoint machines.
This leads to less downtime, increasing productivity among IT staff as well as endpoint machine users.
See Twisted pair.
System Integrator>
A system integrator headquartered in Tampa, Florida.
Parent company Krones manufactures processing equipment.
Hardware>
Sensor>
A device that converts a sensor signal to a standardized output (often 4-20mA) to be able to send it a long distance to a receiver
usually at a central control location.
System Integrator>
A system integrator headquartered in Racine, Wisconsin, with a regional office in Santa Fe Springs, California.
System Integrator>
TriCore’s Automation Engineering & Design division.
TriCore also has Networking, Business & Manufacturing Intelligence (BMI), Engineering Procurement & Construction (EPC), and service & calibration divisions.
Hardware>
Cable>
A cable with one or more pairs of wire that are twisted together in a way that eliminates noise and crosstalk.
If more than one pair is in a cable their twist rate (twists per foot) should be different to minimize crosstalk.
Twister pair cables are inexpensive but also physically fragile.
Pinching, crushing, sharp bends, being stepped on and any repeated flexing will degrade or even destroy cable performance.
Cable care and cable management are important parts of a Hardening Layer One strategy for OEE.
Engineering standard>
A workmanship standard and shop inspection program for electrical industrial control panels
written and administered by Underwriter’s Laboratory.
Any shop certified under this program will make control panels using listed components only and
will assembled using the workmanship standard. Every new panel design is inspected by UL under the program.
Panels assembled under UL 508 will also carry a UL label and will have minimal problems being accepted by
municipal building inspectors.
Standards organization>
A safety certification organization that creates standards and tests products to their requirements.
It is a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory.
The standards most commonly encountered in food processing are:
UL 50 for electrical enclosures.
UL 62 for flexible wire and cable.
UL 489 for molded case circuit breakers.
UL 508 for assembly of industrial control panels.
UL 758 for Appliance Wiring Material, with 7000 different styles already tested.
UL 817 for molded cord sets and power supply cords.
UL 1077 for supplementary circuit breakers.
and many other standards for cables.
A stand-alone battery pack that keep computers and other electronic devices up and running for a limited amount of time until main power is restored. Includes circuitry that manages the charging and discharging of the battery.
Engineering standard>
A standardized quantity of a specific physical property.
A collection of such units for a large number of physical properties is called a system of units.
The two major systems and the metric system (called SI) and the US or Imperial system.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
Schneider Electric's programming software for their M580 line of PLC’s.
See Universal Serial Bus.
Hardware>
Actuator>
Valve>
Operating a valve on and off so that all the surfaces are exposed to the cleaning fluid and that the valve seats and seals are moved to
dislodge any accumulated debris or contamination.
See Valve Cluster.
See Volts Direct Current.
See Valve Group.
qqq A form of Local Area Network that
Networking> A method to extend VLAN’s across networks.
See:
1. Virtual Machine.
2. Valve Matrix.
Hardware>
Sensor>
Typically used in context of 0-10VDC transducer communications.
Original Equipment Manufacturer>
Tetra’s brand of direct UHT processing of aseptic products.
It is an aseptic processing unit for continuous UHT treatment with direct steam injection.
Mainly for heat-sensitive low-acid products such as milk, enriched milk, cream, soy milk, formulated dairy products, ice-cream mix, dairy desserts as well as ESL (extended shelf life) products. The process is also suitable for smooth products like soups, sauces, non-dairy cream, and other starch-based products and can handle smaller particles.
Material handling>
Fluid handling>
Water that has been made pure enough to be part of a medicine that can be injected safely into the human body.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
AVEVA>
Former name for AVEVA software products.
Controls regime>
Schneider Electric>
Current generation of Schneider Electric field I/O products.